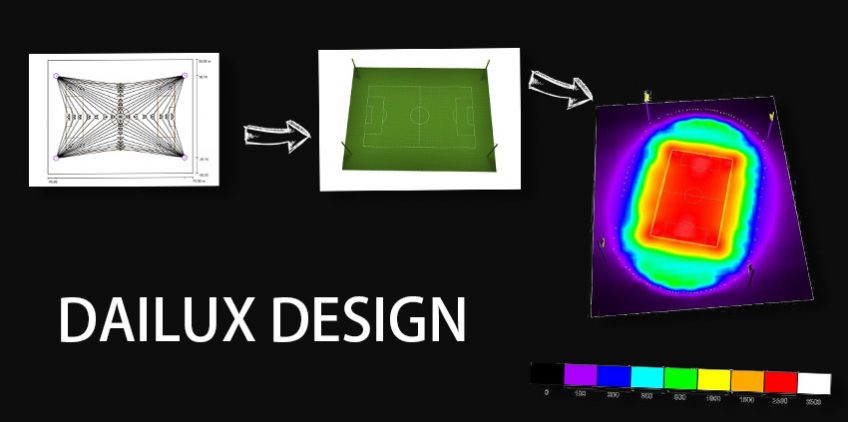
How to understand the lighting design?
How to understand the LED flood light design guidance stadium light design teaching DIAlux simulation guidance standard material
Before a great lighting project is lit, it needs to go through a specific simulation program to design. So for the user, the solution provided by the supplier needs someone to help them understand the design, so that they can understand the designer’s intention. Read on to get an idea of entry-level lighting design.
1.0.1 formulation and principles for the purpose of this standard is in the sports lighting design and construction experience, on the basis of absorbing the international advanced standard, unified lighting design standards and detection methods, improve the quality of sports lighting design, to ensure the use function of sports venues, and safety, advanced technology, reasonable economy, energy saving.
1.0.2 This article stipulates the scope of application of this Standard. According to actual application requirements, this standard applies to stadiums and gymnasiums of major sports events, including lighting design of stadiums and gymnasiums of new construction, expansion and reconstruction as well as lighting detection of stadiums and gymnasiums.
1.0.3 Lighting design and testing of stadiums and gymnasiums shall comply with relevant international Lighting Commission (CIE) standards.It should also comply with international sports organizations such as GAISF, FIFA and IAAF.The requirements of television broadcasters such as The Olympic Broadcasting Service (OBS) and The Beijing Olympic Broadcasting Corporation (BOB) for events and their coverage.
With the construction of a large number of stadiums and gymnasiums gradually improved, lighting design should be carried out according to the actual needs during the construction of stadiums and gymnasiums, taking into account the full use of both during and after the games, so as to achieve both economic and practical purposes.In order to improve the efficiency of use, most stadiums and gymnasiums are multi-functional and multi-purpose, in addition to various sports, they can also be used for non-sports activities, such as concerts and other cultural activities.Large sports facilities can serve activities that accommodate large groups of people and thus benefit them economically.

2 Terms and symbols
2.1.1 Horizontal illuminance
Horizontal illumination.The horizontal illumination on the surface of the court is used to determine the adaptation of the eye within the field of vision and to highlight the visual background of the target (players and objects).
2.1.2 Vertical illuminance
Illumination on a vertical plane.The vertical illumination includes the main camera direction and the secondary camera direction.Vertical illumination is used to simulate the light on the face and body of the athlete, providing optimal recognition to the camera, camera and viewer, and affecting the stereoscopic perception of the illuminated target.
2.1.3 Use illuminance Service Illuminance
The average illumination required to be maintained over a specified surface during the life of a lighting installation.
2.1.4 Maintenance factor maintenance factor
The ratio of the average illuminance or average luminance of a lighting device on a specified surface after a certain period of use to the average illuminance or average luminance obtained on a specified surface when the device is newly installed under the same conditions.
2.1.5 Main camera
A camera used to film important areas of the main or main division.
2.1.6 Auxiliary camera
A camera other than the main camera.
2.1.7 Uniformity of illuminance
Specifies the ratio of minimum illumination to maximum illumination on a surface and the ratio of minimum illumination to average illumination.Uniformity is used to control the level of illumination on the playing field.
2.1.8 Uniformity gradient
The uniformity gradient is expressed by the illuminance ratio of a grid point to its eight neighboring grid points.The uniformity gradient is used to control the change of illumination level between grid points.
2.1.9 Field of play
Sports and ancillary areas enclosed by stands or walls and fences.
2.1.10 Principal Area
The playing area within the underlined area.
2.1.11 Total Area
The main area and the area outside the underlined area.
2.1.12 Competition Area
The main or main division in which the game is played is generally called the field.
2.1.13 Colour rendering index
A measure of the color rendering of a light source.It is expressed by the degree of consistency between the object color under the measured light source and the object color under the reference light source.
2.1.14 General colour Rendering index
The average value of the light source to the color rendering index of the first to the eighth standard color samples stipulated by the International Commission on Lighting (CIE) is generally called the color rendering index.
2.1.15 Special colour rendering index
The color rendering index of the light source for the 9th ~ 15th standard color samples selected by the International Commission on Lighting (CIE).
2.1.16 Colour temperature
When the color of the light source is the same as that of the black body at a certain temperature, the absolute temperature of the black body is the color temperature of the light source.Color temperature is used to describe the sensation or apparent sensation of how warm (red) or cold (blue) a light is.
2.1.17 correlated color temperature correlated see colour temperature
When the color point of the light source is not on the path of the black body, and the color point of the light source is closest to the color point of the black body at a certain temperature, the absolute temperature of the black body is the relevant color temperature of the light source.
2.1.18 Chromaticity
Color properties represented by the International Commission on Lighting (CIE) standard chromaticity system.Color stimulus properties defined by chromaticity coordinates.
2.1.19 Chromaticity coordinates
The ratio of the value of each tristimulus to its sum.In the X, Y, and Z chromaticity system, the excellent coordinates X, Y, and Z can be calculated from the three stimulus values.
2.1.20 Chromaticity tolerances
To represent the deviation of each light source in a batch of light sources from the rated color, denoted by color matching standard deviation SDCM.
2.1.21 Beam Angle
The Angle sandwiched between two vector diameters of a luminescence intensity curve in polar coordinates on a given plane.The luminescence intensity of this sagittal path is equal to 10% of the maximum luminescence intensity.
2.1.22 Aiming Angle
The Angle between the direction of the peak light intensity of the luminaire and the downward perpendicular during lighting design and installation.
2.1.23 Glare
A visual phenomenon that causes discomfort or reduces the ability to observe details or objects because of inappropriate or extreme contrast in the distribution or range of brightness in the field of vision.
2.1.24 Glare Index (glare value)
It is used to measure the subjective response of human eye discomfort to outdoor stadium (or indoor stadium) and other outdoor lighting devices.
2.1.25 TV Emergency Lighting
Lighting used to ensure the continuation of sporting events and television coverage due to a failure of power to normal lighting.
2.1.26 LED Light Emitting Diode Lamp
A semiconductor device that is electroluminescent as a light source.
2.1.27 Stroboscopic effect
Under the illumination of light with a certain frequency, the motion of the object is observed to be different from its actual motion.
2.1.28 Percent flicker ratio Flicker
The difference between the maximum and minimum values of the output optical pass at a certain frequency, expressed as a percentage, as the sum of the maximum and minimum values of the output optical pass.
2.2.1 Illumination
E – illumination;
Eh — horizontal illumination;
Ev – vertical illumination;
Emin — minimum illumination;
Emax — Maximum illumination;
Eave — Average illumination;
Evmai — Vertical illumination of main camera direction;
Evaux — The vertical illumination of auxiliary camera.
2.2.2 Uniformity
U — Uniformity of illumination;
U1 — ratio of minimum illumination to maximum illumination;
U2 — ratio of minimum illumination to average illumination;
Uh — uniformity of horizontal illumination;
Uvmai — Uniformity of illumination in the vertical direction of the main camera;
Uvaux — uniformity of illumination in the vertical direction of auxiliary camera;
UG — uniformity gradient.
2.2.3 Color parameters and glare index
GR — Glare index;
Ra — General color rendering index;
R9 — The color rendering index of the light source for the 9th standard color sample;
Tc – color temperature;
Tcp — Correlation color temperature.
2.2.4 Competition venue
PA — Main competition Area;
TA — General division.
2.2.5 Broadcast on TV
HDTV — High definition television.
3 The basic rules
3.0.1 Stadium lighting shall be classified according to Table 3.0.1 according to the requirements of TV relay and use function.
Table 3.0.1 Stadium lighting classification
|
NO TV broadcasts |
TV broadcasts |
|||
|
Class |
Application |
Class |
Application |
|
|
Ⅰ |
Amateur training |
Ⅳ |
TV broadcasts national games |
|
|
Ⅱ |
Amateur game |
Ⅴ |
TV broadcasts major international matches |
|
|
Ⅲ |
Professional game |
Ⅵ |
HDTV broadcasts major international matches |
|
Note: the Ⅳ level and Ⅴ, Ⅵ shall also apply to other games have special requirements.
3.0.2 Stadium lighting should meet the use requirements of athletes, referees, spectators and other personnel.When there is a television broadcast, the lighting requirements of the television broadcast should be met.
3.0.3 During the high-definition TELEVISION broadcast of major international games, the lighting shall meet the technical requirements of relevant international sports organizations and institutions.
3.0.4 Lighting design of major competition venues shall take special functional lighting requirements into consideration.
3.0.5 The lighting of the stadium shall include the lighting of the competition venue, the auditorium and emergency lighting.
3.0.6 In the design stage of sports building scheme, the requirements of lighting design scheme shall be taken into consideration.
3.0.7 Lighting design of stadiums and gymnasiums should be implemented to save energy while meeting the corresponding lighting targets.
3.0.8 After the installation of lighting system in stadiums and before major competitions, lighting testing shall be conducted.
If you have an ongoing project and want to learn more about this, contact our Green Light team directly.We can provide professional lighting system service for your project, looking forward to your cooperation.
